As a company that provides Blockchain development teams (among other types of teams), we’ve recently come across an increasing number of requests for Blockchain software development, which ultimately inspired us to interview specialists we have working in this field and share the insight we gained from their answers.
Although this technology is in its early days, Blockchain software development has become increasingly popular, resulting in the rise of Blockchain technology companies and startups. In this post, we attempt to get a firm grasp on several questions related to Blockchain development.
For this we have enlisted the aid of Richard James, CCO at Decentr, and Roman K currently working as a Blockchain engineer/RUST specialist.
Decentr is a Blockchain development company that helps users safeguard their data and protect it from prying eyes. Located in the UK, Richard considers Blockchain outsourcing in Ukraine.
Roman K works with CMT Group projects (through nCube as a team vendor), a company that develops a platform for predictive analytics.
The Blockchain development experts have shared their opinion on the following questions:
- What makes Blockchain a secure technology? Being a budding technology, many people wonder how secure it is. We asked our experts their opinion on how Blockchain secures its integrity, so if its security raises questions with you, you can find an answer here.
- What are the most exciting companies/projects on a global scale that use Blockchain? Given the number of requests for Blockchain development services we receive these days, we can assume that Blockchain development is on the rise. Our experts shared which Blockchain technology companies out there are worth watching.
- Why is NFT so popular right now? The NFT craze took the world by storm, so it’s only natural to wonder what stands behind such popularity and if it’s going to have a lasting effect.
- Can Blockchain lead to a better world? No one can tell the future, which is probably why the future intrigues all of us, especially those with a keen interest in technology development. We asked the experts if the potential Blockchain development has to bring positive change to the world.
Richard James, CCO at Decentr, a Blockchain development company
What makes Blockchain so secure?
A Blockchain is essentially a series of blocks that record data in hash functions with timestamps. This makes it very difficult to change or tamper with data. As data cannot be overwritten, the ability to manipulate data is not only extremely impractical but also very difficult to achieve, making data secured on the Blockchain immutable and anonymous. In this way, Blockchain is a purely decentralised network that eliminates centralised points of data attack that cybercriminals routinely target. Blockchain is currently used largely for financial transactions, but the technology shows a great deal more potential. Companies like Decentr are seeking to capitalise on this potential in areas including communications, publishing, advertising, consumer finance etc — anywhere that secure data is of benefit (and with mandatory GDPR/HIPAA compliance, that is everywhere!).
In your opinion, what are the most exciting companies/projects on a global scale that use Blockchain?
The truth is, in over a decade, Blockchain has not fulfilled its promise as foundational Web3 technology; let alone Web4 — and there is no real sign of it doing so with current solutions. In our view, tech companies must aggregate these failings against the potential Blockchain holds in order to achieve cross-chain integration success. This can be achieved by striving to ameliorate the inherent weaknesses of current Blockchain applications in order to build on Blockchain’s strengths with a view to delivering cross-chain solutions to create a foundational next-gen internet. Seen from this perspective, the most influential Blockchain applications are those we have partnered with: Ocean Protocol is a key example as it is a Blockchain-based ecosystem that allows individuals and businesses to easily unlock the value of their data and monetise it through the use of ERC-20 based datatokens. Considering that Decentr is able to deliver far more granular and detailed datasets on behalf of users than any other chain, this company, in conjunction with our cross-chain applications, is setting the future standards for the type of Web3 Blockchain applications the public wants and Web4 business needs.
Why is NFT so popular right now? Do you think that the trend will become the new norm?
NFTs are currently popular as they are able to securely value, purchase and exchange digital art by using a digital ledger. NFTs had their beginnings in online gaming, later with Nike’s patenting of its authenticity (CryptoKicks) and then by the famous Christie’s auction embracing NFT valuation of a digital art piece. In our view, NFTs are a fad that expresses the public desire to be able to digitise further aspects of their lives, in this case art, and NFTs will therefore be redundant when a Blockchain comes along that can make fungible all user data, including art. This is the Blockchain Decentr is building: our Blockchain makes all user data a fungible currency that is accessible to the user – and to no one else except the user — making it uniquely exploitable by users as economic value.
Can Blockchain lead to a better world? If so, in what way?
The promise Blockchain holds for the world, when correctly applied, is to create a true equality of purpose and spirit as defined by immutable and secure user data, which cannot be manipulated, used or abused by third-party actors or agendas for centralised control over individuals and society. This level of security and autonomy, as expressed on the Decentr Blockchain as foundational Web3 technology, means that user data on Decentr becomes a fungible currency, more stable than the dollar of the pound, due to the fact this currency is based on data-as-value and not collective delusion, which is what fiat is currently based on. When this paradigm is realised, the Decentr Blockchain will deliver a user-centric internet and economy, controlled by the individual at the level of every individual, creating true economic and communications autonomy for every connected user.
Roman K, Blockchain developer, CMT group Project
What makes Blockchain so secure?
Blockchains heavily rely on cryptography. One-way hashing allows individuals to submit transactions to the Blockchain without exposing their passwords or private keys.
Another aspect of Blockchain’s security is immutability. Once a record of the transaction has been written to the chain, it is irreversible and will be stored there forever. And probably the most important security mechanism, which is built into Blockchains by design, is decentralization. This means that anyone in the world can run validator/mining nodes, which confirm new transactions to the chain. This prevents a single government or business entity from imposing censorship on particular users or transactions.
In your opinion, what are the most exciting companies/projects on a global scale that use Blockchain?
- Dfinity: Distributed computing and running of web applications.
- Audius: A streaming platform for musicians.
- InterPlanetary File System (IPFS): Distributed file storage.
- Omega Grid: A tool for energy businesses and individuals to manage peer-to-peer energy sales.
Why is NFT so popular right now? Do you think that the trend will become the new norm?
Due to the nature of decentralized markets, NFTs have become a way for less known creators to capitalize on their work removing broker and distribution fees from the equation. One can draw a parallel with crowdfunding tools, where individuals all across the world can support the cause, inject capital into projects regardless of project’s location. Same with NFTs, individuals can support creators around the globe by buying their artwork, music, etc.
The main problem with NFTs arises when individuals start treating them as investing instruments rather than collector’s items. Similar to fine wine and high-end art markets, NFT markets are mostly illiquid. Meaning that, if an individual decides to realize gains on NFT speculation, it will take some time to match his ask with a buyer keeping his investment capital locked in.
NFTs are definitely here to stay. The most important obstacle for them to overcome is to decouple from cryptocurrency prices and speculation. As soon as that happens, NFTs will be able to find new applications in our day-to-day lives.
Can Blockchain lead to a better world? If so, in what way?
Blockchain has created many facilitations already by providing a way to exchange data in a fast and secure fashion. But to answer this question, one should answer whether it is a good idea to shift governing power from institutions to individuals. Let’s take the financial system as an example. Blockchain has created a separate economy where the issuance of the assets is not controlled by any central entity. The low barrier entrance allows literally anyone to be a part of this ecosystem. This is great for citizens of the countries where the economy is undergoing scrutiny. With Blockchain, they get an opportunity to store the financial value of their holdings and avoid the ongoing crisis. However, the removal of censorship in Blockchain also allows bad actors to use this system for their own purposes, which sometimes can involve real-world crimes.
So, in general, the Blockchain can lead to a better world where many of our day-to-day activities will become more secure and decentralized, but there is still a long road ahead to properly integrate it.
Over to you
Where do you stand on Blockchain development? If it is one of your priorities, we at nCube can step in and build the right kind of team to implement Blockchain technology for you. Our model includes direct access to your Blockchain developers, so they will be an extension of your company, working for you full-time 40 hours per week. Let’s connect.
Changes in global markets and advances in technology have changed how offshore information technology companies work. While the geographic location is an essential consideration in other industries, organizations in the IT industry are much more open to a multi-location structure and hiring offshore developers. That means IT companies can capitalize on the strengths of each of their sites.
During its early years, companies considered IT offshoring to take advantage of lower overhead and potential growth. However, as technology took over the world, more and more organizations began to increase their investments in IT. Eventually, hiring offshore developers became a viable option.
The last decade brought significant changes to how businesses used and consumed IT products and resources. The advent of cloud technology improved global communication, and even the increased interconnection of global cultures have significantly changed IT offshoring work.
In this article, we will take a look at our findings on the current state of IT offshoring and outsourcing, including recent trends, driving forces, and what changed in the past years
Outsourcing vs. offshore developers
You may be asking companies to use offshoring to do what? Well, back in the early years of offshoring and outsourcing, the two business processes are easily separated. However, as globalization and internationalization permeated practically every industry, various concepts have begun to float around, blurring the line between the two.
Traditionally, offshoring refers to the organization’s movement of its activities abroad. On the other hand, outsourcing means moving activities to an offshore developers provider, regardless of its location.
However, recent decades have changed these definitions drastically. Companies that use offshore developers have combined all or parts of business offshoring and outsourcing processes to become interchangeable. That gave way to concepts such as multi-sourcing, offshore outsourcing, nearshoring, offshore IT companies, offshore software development, selective sourcing, and more.
To simplify, we define offshoring and outsourcing as providing administrative services in locations abroad, whether through an in-house department or a third-party service provider. Companies often have teams worldwide, usually combining internal teams working remotely and offshore developers hired through outsourcing entities. Hence, we will use offshoring to refer to all the concepts described above from this point on.
The current state of offshore information technology and related industries
Offshoring is not a modern phenomenon. Each generation has different motives attributed to market demands, technological advancements, and cultural intermingling.
In the past, offshoring was centered around goods. Organizations take advantage of affordable production costs and efficient distribution networks. For example, Sweden has long been known to be a popular offshoring destination for organizations in the shipbuilding, textile, and manufacturing industries in Europe.
However, modern-day offshoring efforts are driven by offshore information technology rather than goods. Thus, there was a noticeable shift in the driving forces between the late ’80s and early ’90s, which continues to this day.
First, and obviously, such low costs drive companies to consider offshore software development to maximize their profits. Second, countries outside the United States are beginning to develop their own offshore IT companies. These budding markets are perfect grounds where established companies can take new roots before prices go up. Lastly, unique factors such as excellent yet affordable infrastructure, advanced technologies, similar culture, language, and other special competencies drive companies to relate some parts of their organization, specifically the offshore information technology units.
The global state of offshore IT companies

Closely related to IT services are business processes that are commonly outsourced to BPO’s abroad. So much so that entire BPO industries have developed in India, the Philippines, and most Eastern Europe. As such, global offshore software development expenses have steadily increased throughout the years.
Since 2000, the influx of organizations entering new locations has pushed offshore information technology to new heights.
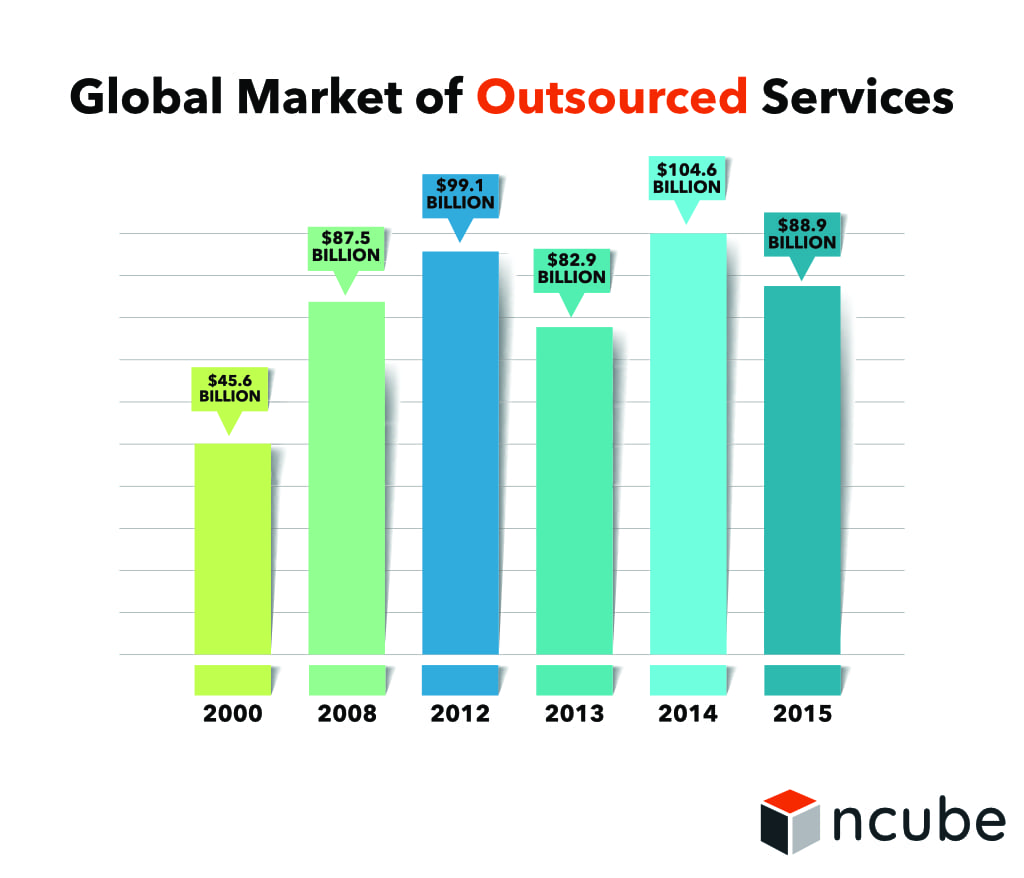
However, 2016 recorded the worst market report with only $76.9 billion, the lowest in a decade. The primary motivation of the decreasing market was the effort to cut costs and focus on core business processes. This means more organizations are spending more on new solutions through IT services than on offshore developers.

The trends in offshore IT companies had exciting effects on the IT industry. In 2018, business process outsourcing had a much smaller market share than information technology offshoring. The BPO industry only contributed $23.6 billion compared to the offshore information technology’s $62 billion offshoring revenue.
The 2017 report of the most outsourced and offshored services of IT leaders worldwide reflects this trend as well. Software application development took the top spot at 64 percent. Similarly, IT functions dominate the top offshored services in the last few years.
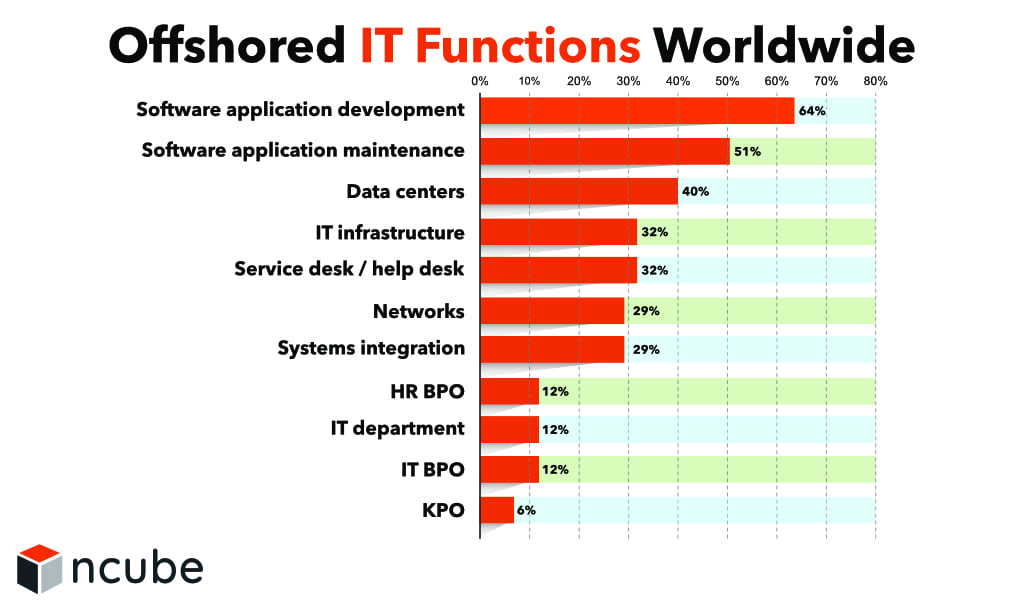
Interestingly, there is a rising trend in the IT offshoring business in recent years. Between 2017 and 2018, there is a slight drop in allotted budgets for offshore software development. Even with large companies increasing their total expenditures, medium and small companies are turning to cloud technology, which is much more affordable.
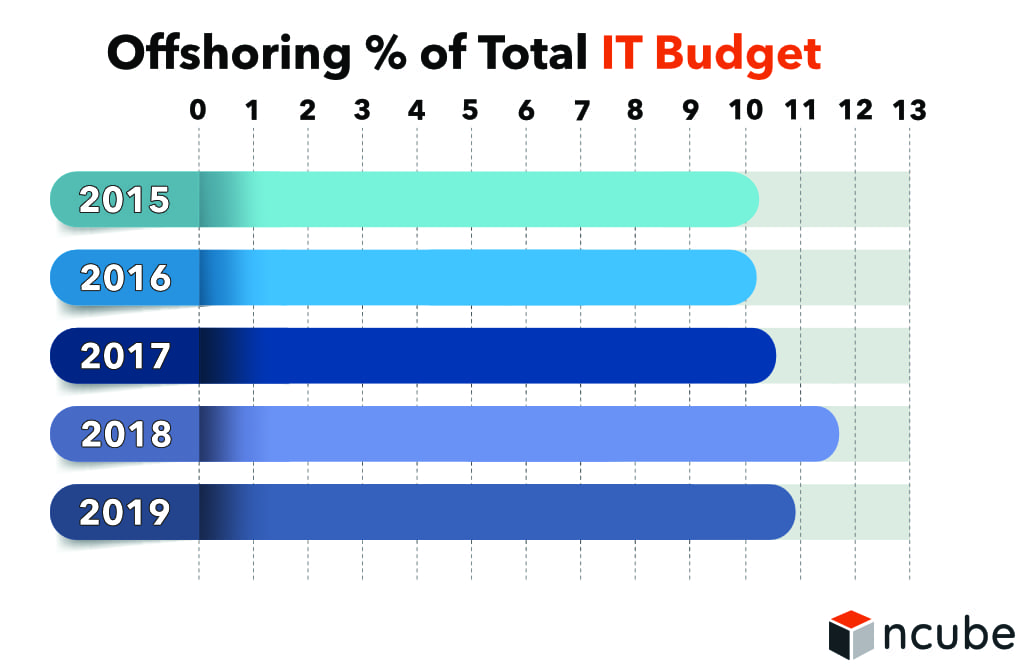
Again, this recent trend seems to reflect the prediction during 2016 when cloud technology is taking off rapidly and set to disrupt the global market.
Offshore developers: training and opportunities
With the move from exclusively outsourcing from the labor force to offshoring IT services, offshore developers have become the top export of most outsourcing countries. In the above graph, access to intellectual capital is one of the driving forces of offshore IT companies.
The skill level and prices are top priorities in hiring offshore teams. Eastern Europe and the surrounding regions are known to be excellent sources of top offshore developers in the West. Russia, Ukraine, and Poland are leading the pack with exceptional offshore developers who possess business knowledge and communication.
Additionally, Latin America is a favorable region for companies that do not want to deal with severe time differences. Brazil is becoming a leading country for offshore developers specialized in Ruby, which is always in demand.
Hire software
Finally, Asia has always been a hotbed of offshore software development with BPO’s and offshore IT organizations targeting countries like India and China even during the early years of outsourcing. Even with significant language barriers, more and more businesses are considering relocation in this region due to affordable business operation costs. Also, more and more countries are emerging in the IT sector and offshoring markets such as Pakistan, the Philippines, Thailand, and more.
Offshore developers: opportunities

As with recent innovations in communication, cloud technology, and infrastructure, we do not see IT offshoring slowing down any time soon. As more areas become viable offshore developers’ pools of IT skills, companies are beginning to look at countries beyond offshore software development.
Organizations are beginning to realize the advantages of hiring offshore developers. Even small and medium-sized companies are looking at IT solutions developed by offshore developers and IT professionals outside their location.
Just like the difference between offshoring and outsourcing, geographical limitations are blurred, allowing organizations to set up offshore software development units across the world. Let’s take a look at one of the rising IT talent sources in Europe: Ukraine.
Offshoring spotlight: Ukrainian offshore developers
In recent years, Ukraine has been one of the top countries as the primary destinations of IT offshoring companies. As a result, the country is poised to compete with India and China in offshore developers’ availability and training in information technology.
Our observation in the last five years showed an increase of about 20 percent in human capital in the Ukrainian offshore IT companies. Since 2011, the IT sector has doubled with more fresh talents coming in every year.
Nowadays, more and more companies have offshore developers across Europe, just like nCube. With offices in both London and Kyiv, the company is able to take advantage of top-quality talent and high-profile clients across the region. The organization comprises senior offshore developers and Master’s degree holders, with 70% certified senior offshore developers. That reflects the country’s top-notch training in IT and related professional consultants.
nCube’s remote teams are experts in Java, Go, Javascript, Python, and .NET, which are the most in-demand programming languages right now. Organizations inside and outside Europe can build a remote team of offshore developers to create custom software for their specific needs.
Along with expertise in offshore software development, the company is also delving into emerging industries like blockchain and Internet-of-Things. As exemplified by nCube, Ukrainian offshore developers are becoming leaders in bleeding-edge technology.
Offshore IT companies: Final Thoughts
IT offshoring will continue to shift as new technologies emerge. Regardless of the current trends, we see an ever-expanding industry ripe with many opportunities for both businesses and the workforce. Organizations are no longer limited by their locations. In the future, we expect to see a further redefinition of offshore IT companies and outsourcing processes as the industry continues to snowball.
Companies looking for outsourcing opportunities in Ukraine are always curious about the country’s legislation. One of the primary fears, and often misconceptions about Ukraine is that the country relies heavily on “out of date legislation”, and practices inherited from the Soviet Union. Although understandable, the government has made significant steps towards improving processes, and creating favorable conditions for international cooperation. As a result of those efforts, Ukraine has become home to over 12,500 IT companies, most of whom are providing software development services for organizations around the globe. Not only has Ukraine fostered the growth of homegrown talent such as Grammarly, Petcube and Deposit photos, Ukraine has become home to global brands such as Samsung, Wargaming, ABBYY, Rakuten, and many more.
Whether you want to hire a developer or are looking for outsourcing opportunities, this article will give you an idea of the baseline legal aspects of hiring in Ukraine.
Working hours | Conditions
Like in many European countries, a full-time employee in Ukraine works 8 hours per day, which amounts to 40 hours per week. Employees are to take a 1-hour unpaid lunch break after 4 hours of work. According to the Labor Law of Ukraine, overtime is allowed in exceptional cases and in many cases is limited to 4 hours of overtime within two days in a row. The law also requires employers to pay a double wage rate for overtime. Of course, this regulation applies neither to freelancers nor self-employed workers. With this in mind, many companies strive to create a stable workflow and take anti-burnout measures, ensuring employees don’t wind up stretched out too thin.
Infrastructure

IQ business center, Kyiv
IT companies are among the biggest tenants of business centers in Ukraine. Downtown Kyiv is filled with modern business centers occupied by IT companies of all sizes. The city offers several classes of business centers, such as A, B and C. IT companies typically occupy cream-of-the crop offices within A and B class premises.
Location:
Class A: Kyiv downtown.
Class B: Along the main urban highways.
Building:
Class A: A new building: 3 or less years in occupation.
Class B: A new or reconstructed building: 4–7 years in occupation.
Premises management:
Class A: Professional building management according to international standards.
Class B: Professional maintenance service.
Security:
Class A: 24/7 security, modern security systems, and automated access control to premises.
Class B: 24/7 security, modern security systems.
Parking:
Class A: Guarded ground-level and underground parking.
Class B: Guarded ground-level parking.
In addition, business centers provide the following amenities:
- Ergonomic office furniture;
- Workstations with modern PCs or laptops;
- Meeting rooms equipped with video conferencing facilities;
- Conference rooms;
- Receptionist desk and guest welcoming zone;
- Dining area with a microwave, tea and coffee making facilities;
- Break rooms with a Playstation, TV, VR helms, tennis tables, massage chairs, etc;
- Office cleaning and maintenance.
Not only does it create a reliable infrastructure for doing business but also ensures pleasant working conditions for employees. Essentially, Kyiv has a reliable Internet connection, with a download speed of 67.27 Mb per second and 70.14 Mb per second upload speed.
Data protection
Many IT companies in Ukraine deal with the personal data of European citizens. Thus, a reasonable question arises, is data protection regulated in any way?
Yes, it is. First of all, the country legislates data protection via the act “On Personal Data Protection” passed in 2010. Secondly, given that GDPR directly affects outsourcing companies, the government has introduced a range of changes to Data Protection Legislation aimed to whip it into shape and make it compliant with European standards. We can now observe a full alignment of the Ukrainian legal system with the EU Data Protection Doctrine.
Moreover, following the new data protection standards promoted by GDPR, many IT companies have invested both time and resources into bringing their activities and strategies in line with the GDPR.
While Canadian data protection law, PIPEDA, has a lot in common with GDPR, which most Ukrainian companies are familiar with, the common concern relates to USA data regulations. Since data protection in the USA is regulated by a wide range of federal and state laws, outsourcing companies have to go the extra mile to be compliant with regulations valid in their clients’ location. Thus, data protection should always be detailed in the Service Agreement, especially when it comes to Health Insurance Portability and Accountability (HIPAA) regulations.
Days off
Holidays. Employees can take a maximum of 24 calendar days of paid leave per year after the first 6 months of employment. In Ukrainian IT companies, where projects’ needs should always come first, contractors usually plan and negotiate vacations with managers/team leads on the client’s side in advance. Overall, Ukrainian developers, on the caveat of passing the probation period (typically, from 1 to 3 months), can take up to 20 days of paid leave per annum.
Public holidays. There are ten public holidays observed in Ukraine. The most important rule here is that when a public holiday falls on a Saturday or Sunday, it’s usually moved to the following Monday. For example, since Easter is celebrated on a Sunday, the following Monday is an extra holiday.
Sick leaves. In Ukraine, employees are paid while being on sick leave. The allowance ranges between 50% to 100% of an employee’s average salary. The law requires providing a doctor’s note issued on the first day of sickness to be entitled to compensation.
When it comes to contractors working in IT, the sick leave policy can vary, given that each employer decides on their own rules regarding sick leaves and compensation. In many cases, the employer compensates up to 10 days in sick leaves. It’s also worth mentioning that most IT companies in Ukraine provide health insurance as an employee benefit assuming free treatment for common illnesses.
Taxation
Ukraine has significant income taxes, constituting roughly 40% of an employee’s salary. Yet, there’s a flat tax system for self-employed specialists: 5% of income. That’s why, in most cases, Ukrainian developers working at outsourcing companies are registered as self-employed contractors, which makes them eligible for a 5% tax. Companies typically compensate for a tax fee by including it into the employee’s salary. When you hire developers in Ukraine, the employment taxes usually fall on the vendor’s shoulders, which is a good way to cut costs compared to an in-house team in Europe or North America.
Wrap up
Since IT generates significant value from foreign exchange, the government actively supports the industry by reforming laws on employment, taxation, and data protection.
Most Ukrainian IT companies follow the Labor Law of Ukraine regulations regarding working hours, breaks, holidays, sick leaves, and vacations, simply because they make sense and promote a healthy work-life balance. Nevertheless, each company offers individual benefit packages to attract developers to come and work for them. The benefits only improve from year to year, given the fierce competition for the top tech talent among IT companies.
If you have any questions (or concerns) regarding legal aspects of working with Ukrainian developers, just drop us a line, and we’ll be happy to address them. Let’s connect.
Ukraine has an eventful history of mobile communication. It goes back to establishing the first telephone exchange in Kyiv and continues with modern-day mobile Internet providers and the 5G network. In this post, we take a look at significant milestones in Ukrainian telecommunication and the prospects for the industry’s future.
The early days: History of Ukraine’s landline
Our story begins in the late 19th century when the first telephone stations opened in three cities: Odesa (1882), Kyiv and Lviv (both in 1884). Two years later, the forerunner of the modern telecommunication system saw the light of the day. It was the first full-fledged city telephone network built in Kyiv (1886).
During the 20th century, the capacity of the Kyiv telephone network grew from 300 numbers to over 4,000 numbers. As the demand continued to go up, modernization of the urban telecommunication system was inevitable.
As such, between 1912-1914, reconstruction took place, which improved call quality and brought on new users.
However, the First World War and the post-war period put a damper on telecommunications’ development, only to be revived in the 30s. During this decade, the capacity of the network grew to 22,400 numbers serviced by four exchange stations that were eventually destroyed soon after World War Two began.
Reconstruction began in the aftermath of World War Two in the early 40s, and since then, nothing could stop the evolution of telecommunication. By the mid-60s, Kyiv was able to serve 800,000 numbers in a city of 1.1 M people.
The 90s: The era of portable phones
Cell phone communication in Ukraine kicked off in the early 90s when UMC, a joint Ukrainian-Dutch telecommunications company, arrived on the market. By the time the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991, the mobile operator put up six stations for delivering 1G cell communication standard.
This culminated in a landmark event, highlighted by a 40-second call made by the first President of Ukraine, Leonid Kravchuk to the Ukrainian Ambassador in Germany at the time, Ivan Piskov.
The event wasn’t met with much excitement, though. At that time, there was only one cell phone per 18,000 people. It would be years until on-the-go communication broke the confines of business use.
Nevertheless, Ukraine kept pace with the world’s trends in telecommunication. In 1994, a nation-wide mobile operator, Kyivstar, was founded. It laid the groundwork for communication taking over Ukraine, first in the business sphere and then slowly but steadily permeating our daily lives.
A few years later, Ukraine reached another milestone: The first Internet provider, Golden Telecom, enters the market, creating the very first corporate networks. However, back in 1996, the Internet was far from being ubiquitous, given its slow speed and sky-high prices.
People began to exchange text messages in 1998, and the same year commercial SIM cards hit the market. The idea of being reached by phone, wherever you are, gradually set in, and the demand went up.
Finally, by the end of the Millenium cell phones go en masse, as the cost of mobile communication drops.
The 2000s: Mobile Internet becomes available
The 2000s is a remarkable decade that digitized the world. We can observe a boost in mobile communication in Ukraine during this time. By 2004, there were 12 M users served by three mobile operators: Kyivstar, Djuice, and Jeans. Finally, by 2006, mobile phones were no longer seen as attributes of business and wealth, as from 2004 to 2006 the number tripled to nearly 36 M.
Once Apple disrupted the industry in 2007, it didn’t take long for Ukraine to join the smartphone bandwagon. Just as anywhere in the world, Ukrainians began to use the mobile Internet for daily communication.
The 2010s: The introduction of 3G in Ukraine
The next decade brought down the curtain on traditional telephones. The number of payphones over the country reduced from 56,000 to 6,000. It’s only natural, given that mobile operators began to provide 3G, and the speed of the Internet skyrocketed. The new-generation standard of mobile internet has drastically changed how Ukrainians’ communicate and prompted mobile operators to modernize their infrastructure.
The next milestone for Ukraine was 4G, which the country started to adopt in 2015. By 2018, three out of six mobile operators launched the 4G standard, which revolutionized mobile communication even more.
Mobile communication in Ukraine in 2021 and beyond
According to recent data, Ukraine has 55 M mobile operator subscribers in total. Currently, mobile operators include companies like Kyivstar, Vodafone, Lifecell, Intertelecom, Trimob, and PeopleNet.
The speed of mobile Internet in Ukraine is being continually improved. 4G permeates all spheres of life: from leisure to telemedicine and reaches far-off rural areas in all regions of Ukraine. According to the memorandum signed by the government and mobile operators, 95% of Ukraine’s population will get access to 4G by the end of 2021.
It’s also worth mentioning that Ukraine ranks 4th in the world for the cheapest mobile Internet, and tops the list of countries with the cheapest fixed-line broadband.
What’s next?
In 2020, the government approved an action plan for 5G implementation. A tender for obtaining a relevant license will be held at the end of 2021.
Ukraine’s major mobile operators (Kyivstar, Lifecell, and Vodafone), aim to implement 5G at some point in the future. However, a nation-scale 4G network remains a top priority for most operators for the time being.
Vodafone believes that over the next few years, 4G will remain the primary data transmission technology. The company says it’s better off investing in a 4G network nation-wide rather than in isolated 5G points. However, if Vodafone gets the frequencies necessary for implementing 5G via the tender, the chances are high that 5G from Vodafone will appear as early as 2022.
Lifecell is also an advocate of implementing 4G first, saying that 5G is only needed for machine-to-machine communication on an industrial scale. Yet, the company has already deployed a 5G test segment in their office to explore the technology’s capabilities in the current environment. However, the company firmly believes that they need to fulfill their obligations to provide 4G coverage throughout the country before diving into full-blown 5G implementation.
Kyivstar, alongside its competitors, believes that 4G is powerful enough to meet the demands of most users, such as IoT networks, wireless broadband access, B2C gaming, VR, and private B2B networks. However, the company plans to keep an eye on a license tender. In case of winning, Ukrainians may see the 5G standard from Kyivstar in 2023 or later.
Despite the fact that the telecommunication industry in Ukraine is highly regulated, mobile operators strive to overcome obstacles on their way towards the ubiquity of the services in all parts of the country. It looks like the next milestone for Ukraine is 4G, while the prospects of implementing 5G remain uncertain. Still, we can say that the major players are adopting modern technologies to stay relevant and not to lose positions on the market. For that, they rely heavily on Ukraine’s pool of tech talent. In particular, data scientists and machine learning specialists are in high demand.
Our clients say that good software developers are scarce and finding the right people for a project is not easy. Those who are comfortable with a remote environment are considering hiring from the world’s pool of talent. And those that already have experience in running remote teams might want to give IT outsourcing Ukraine a try. In this article, we take a look at cases in which involving software developers in Ukraine will make sense for your business.
Reason 1. When you are disappointed in cheap providers
We’ve heard a lot from our customers that the major drawbacks of cheap providers are low-quality code and a lack of project ownership. The tech scene indeed is booming, with lots of underqualified software engineers joining the ranks. Our engineers occasionally complain about the code they have to fix after Asia-based developers, which slows down the client’s project. Eastern Europe doesn’t have an equal workforce in terms of quantity, but it definitely provides highly qualified engineers. Ukrainian developers come from the country’s strongest technological schools, and many of them have contributed to Ukraine technology development.
Reason 2. When you want the engineers to really augment your team
If you are browsing IT companies in Ukraine, you probably don’t want it to be another “body shop”. You want to build a team that would share your company culture and is passionate about what you do. In other words, you want the remote team to be Your Team.
It’s true that the team needs to be a natural extension of your core development team and develop a sense of ownership for your project. Ukrainian developers are comfortable with adapting to the work style of the Client’s team. As such, it can really be your team – from corporate banners on the walls to the members with a mindset that resonates with your values.
Reason 3. When you want to feel like your virtual team is next door
Ukraine is located in the GMT+3 time zone which is very convenient when it comes to synchronizing with Europe-based clients. Working with North American companies, software developers Ukraine usually shift the start of the working day till afternoon to have more cross-hours with the head offices.
Geographical proximity in software engineering outsourcing plays a key role. Kiev has two international airports from where you can travel to more than 80 destinations. Wherever your business is located, the team visits will be convenient. For example, the flight to London takes less than 4 hours and nearly 10 hours to New York.
Coupled with daily video conferences and regular communication, it’s simple to create a sense of a strong connection between the distributed teams. Also, the engineers can frequently travel to your head office for training and important meetings.
Reason 4. When you want to speak the same language with your remote engineers
Software engineering outsource demands profound English skills. To land a job in the landscape of programming outsourcing, it is essential to master English to write and read software requirements specifications in this language. Unlike their Asian counterparts, Ukrainian developers have good English skills – almost 80% of specialists have an Intermediate or higher proficiency. Communicating without the language barrier means saving time for development instead of spending hours translating the documentation.
Reason 5. When you want to build a team with a Western mindset
Computer science outsourcing to Ukraine plays by the customer company’s rules. It’s a fact that Ukrainian developers thrive working under the Western management style. As long as you invest in their professional development, they will be happy working with you. As a nation, Ukrainians have an affinity with European mindset, valuing work-life balance but treating their work in all seriousness.
Our clients value Ukrainian developers for the hard-working nature and problem-solving approach. They also point out the outspokenness as in being ready to share the concerns directly with the Client.
In conclusion: Outsourcing developers with NCube

Backed by our experience at NCube, it makes sense to hire Ukrainian developers when you want to:
- Nurture a remote culture similar to the one you have in-house
- When you want your developers to share the passion for what your company does
- Have a team that really augments your own development team instead of a body shop
- Have remote engineers that will work effectively during the cross-over hours
- Outsource computer programming to specialists with solid education background and English skills

