As a company that provides Blockchain development teams (among other types of teams), we’ve recently come across an increasing number of requests for Blockchain software development, which ultimately inspired us to interview specialists we have working in this field and share the insight we gained from their answers.
Although this technology is in its early days, Blockchain software development has become increasingly popular, resulting in the rise of Blockchain technology companies and startups. In this post, we attempt to get a firm grasp on several questions related to Blockchain development.
For this we have enlisted the aid of Richard James, CCO at Decentr, and Roman K currently working as a Blockchain engineer/RUST specialist.
Decentr is a Blockchain development company that helps users safeguard their data and protect it from prying eyes. Located in the UK, Richard considers Blockchain outsourcing in Ukraine.
Roman K works with CMT Group projects (through nCube as a team vendor), a company that develops a platform for predictive analytics.
The Blockchain development experts have shared their opinion on the following questions:
- What makes Blockchain a secure technology? Being a budding technology, many people wonder how secure it is. We asked our experts their opinion on how Blockchain secures its integrity, so if its security raises questions with you, you can find an answer here.
- What are the most exciting companies/projects on a global scale that use Blockchain? Given the number of requests for Blockchain development services we receive these days, we can assume that Blockchain development is on the rise. Our experts shared which Blockchain technology companies out there are worth watching.
- Why is NFT so popular right now? The NFT craze took the world by storm, so it’s only natural to wonder what stands behind such popularity and if it’s going to have a lasting effect.
- Can Blockchain lead to a better world? No one can tell the future, which is probably why the future intrigues all of us, especially those with a keen interest in technology development. We asked the experts if the potential Blockchain development has to bring positive change to the world.
Richard James, CCO at Decentr, a Blockchain development company
What makes Blockchain so secure?
A Blockchain is essentially a series of blocks that record data in hash functions with timestamps. This makes it very difficult to change or tamper with data. As data cannot be overwritten, the ability to manipulate data is not only extremely impractical but also very difficult to achieve, making data secured on the Blockchain immutable and anonymous. In this way, Blockchain is a purely decentralised network that eliminates centralised points of data attack that cybercriminals routinely target. Blockchain is currently used largely for financial transactions, but the technology shows a great deal more potential. Companies like Decentr are seeking to capitalise on this potential in areas including communications, publishing, advertising, consumer finance etc — anywhere that secure data is of benefit (and with mandatory GDPR/HIPAA compliance, that is everywhere!).
In your opinion, what are the most exciting companies/projects on a global scale that use Blockchain?
The truth is, in over a decade, Blockchain has not fulfilled its promise as foundational Web3 technology; let alone Web4 — and there is no real sign of it doing so with current solutions. In our view, tech companies must aggregate these failings against the potential Blockchain holds in order to achieve cross-chain integration success. This can be achieved by striving to ameliorate the inherent weaknesses of current Blockchain applications in order to build on Blockchain’s strengths with a view to delivering cross-chain solutions to create a foundational next-gen internet. Seen from this perspective, the most influential Blockchain applications are those we have partnered with: Ocean Protocol is a key example as it is a Blockchain-based ecosystem that allows individuals and businesses to easily unlock the value of their data and monetise it through the use of ERC-20 based datatokens. Considering that Decentr is able to deliver far more granular and detailed datasets on behalf of users than any other chain, this company, in conjunction with our cross-chain applications, is setting the future standards for the type of Web3 Blockchain applications the public wants and Web4 business needs.
Why is NFT so popular right now? Do you think that the trend will become the new norm?
NFTs are currently popular as they are able to securely value, purchase and exchange digital art by using a digital ledger. NFTs had their beginnings in online gaming, later with Nike’s patenting of its authenticity (CryptoKicks) and then by the famous Christie’s auction embracing NFT valuation of a digital art piece. In our view, NFTs are a fad that expresses the public desire to be able to digitise further aspects of their lives, in this case art, and NFTs will therefore be redundant when a Blockchain comes along that can make fungible all user data, including art. This is the Blockchain Decentr is building: our Blockchain makes all user data a fungible currency that is accessible to the user – and to no one else except the user — making it uniquely exploitable by users as economic value.
Can Blockchain lead to a better world? If so, in what way?
The promise Blockchain holds for the world, when correctly applied, is to create a true equality of purpose and spirit as defined by immutable and secure user data, which cannot be manipulated, used or abused by third-party actors or agendas for centralised control over individuals and society. This level of security and autonomy, as expressed on the Decentr Blockchain as foundational Web3 technology, means that user data on Decentr becomes a fungible currency, more stable than the dollar of the pound, due to the fact this currency is based on data-as-value and not collective delusion, which is what fiat is currently based on. When this paradigm is realised, the Decentr Blockchain will deliver a user-centric internet and economy, controlled by the individual at the level of every individual, creating true economic and communications autonomy for every connected user.
Roman K, Blockchain developer, CMT group Project
What makes Blockchain so secure?
Blockchains heavily rely on cryptography. One-way hashing allows individuals to submit transactions to the Blockchain without exposing their passwords or private keys.
Another aspect of Blockchain’s security is immutability. Once a record of the transaction has been written to the chain, it is irreversible and will be stored there forever. And probably the most important security mechanism, which is built into Blockchains by design, is decentralization. This means that anyone in the world can run validator/mining nodes, which confirm new transactions to the chain. This prevents a single government or business entity from imposing censorship on particular users or transactions.
In your opinion, what are the most exciting companies/projects on a global scale that use Blockchain?
- Dfinity: Distributed computing and running of web applications.
- Audius: A streaming platform for musicians.
- InterPlanetary File System (IPFS): Distributed file storage.
- Omega Grid: A tool for energy businesses and individuals to manage peer-to-peer energy sales.
Why is NFT so popular right now? Do you think that the trend will become the new norm?
Due to the nature of decentralized markets, NFTs have become a way for less known creators to capitalize on their work removing broker and distribution fees from the equation. One can draw a parallel with crowdfunding tools, where individuals all across the world can support the cause, inject capital into projects regardless of project’s location. Same with NFTs, individuals can support creators around the globe by buying their artwork, music, etc.
The main problem with NFTs arises when individuals start treating them as investing instruments rather than collector’s items. Similar to fine wine and high-end art markets, NFT markets are mostly illiquid. Meaning that, if an individual decides to realize gains on NFT speculation, it will take some time to match his ask with a buyer keeping his investment capital locked in.
NFTs are definitely here to stay. The most important obstacle for them to overcome is to decouple from cryptocurrency prices and speculation. As soon as that happens, NFTs will be able to find new applications in our day-to-day lives.
Can Blockchain lead to a better world? If so, in what way?
Blockchain has created many facilitations already by providing a way to exchange data in a fast and secure fashion. But to answer this question, one should answer whether it is a good idea to shift governing power from institutions to individuals. Let’s take the financial system as an example. Blockchain has created a separate economy where the issuance of the assets is not controlled by any central entity. The low barrier entrance allows literally anyone to be a part of this ecosystem. This is great for citizens of the countries where the economy is undergoing scrutiny. With Blockchain, they get an opportunity to store the financial value of their holdings and avoid the ongoing crisis. However, the removal of censorship in Blockchain also allows bad actors to use this system for their own purposes, which sometimes can involve real-world crimes.
So, in general, the Blockchain can lead to a better world where many of our day-to-day activities will become more secure and decentralized, but there is still a long road ahead to properly integrate it.
Over to you
Where do you stand on Blockchain development? If it is one of your priorities, we at nCube can step in and build the right kind of team to implement Blockchain technology for you. Our model includes direct access to your Blockchain developers, so they will be an extension of your company, working for you full-time 40 hours per week. Let’s connect.
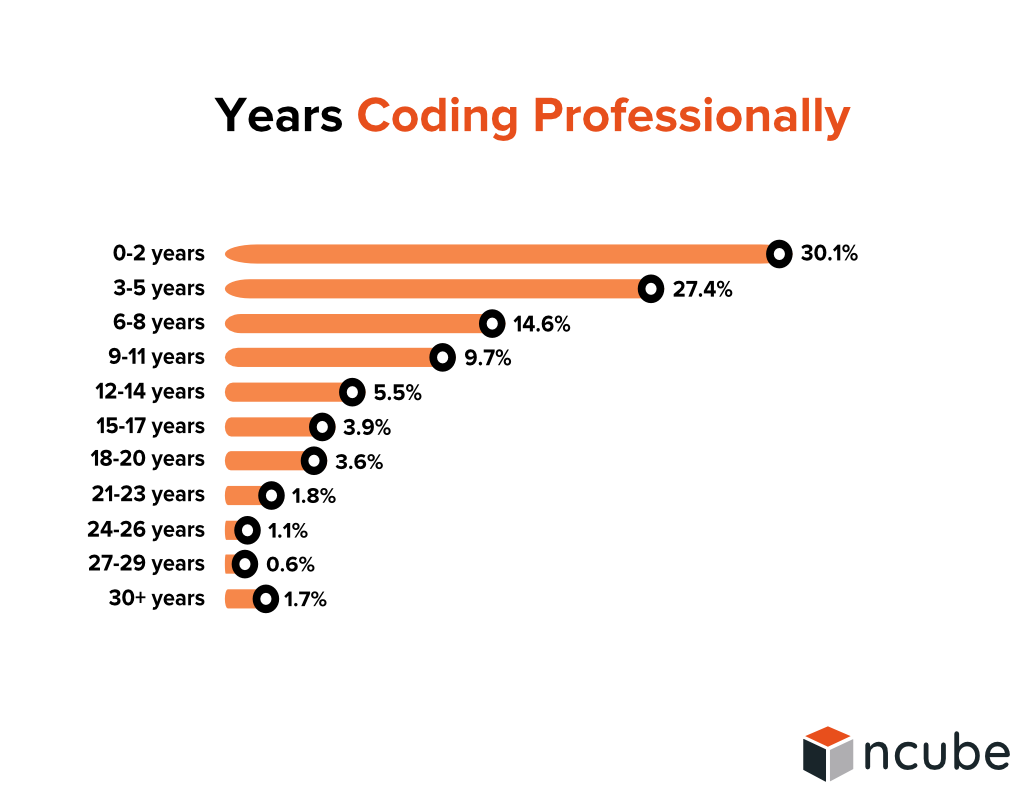
Current state of the software developer job market
In the USA alone, there is, at this moment, almost 500,000 software developer jobs on the market. It’s estimated that another 500,000 software developers will retire in the next few years. That means that there will be a shortage of one million software developers in the USA. The estimate is that by 2021, there will be a shortage of 1.4 million software developers and only 400,000 software developer graduates. Employment of software developers is projected to grow 21 percent from 2018 to 2028, much faster than the average for all occupations.
Software development is a lucrative career path with an average annual salary of $99,500. The demand for software engineers is increasing, but there aren’t enough skilled engineers to fill the demand. What does that mean for the average software development company?

They will have to make even more lucrative offers to fill void positions. A shortage of software engineers worldwide means their average salaries will keep increasing. That isn’t a good thing for companies because it doesn’t mean an increase in the skill of the average worker.
Because of this talent shortage, the current talent pool will continue to deliver average workers who will demand high payment.
According toITWorld, a company can spend 8-12 weeks or longer when hiring a specialized team of software developers. This is two or three months wasted, project launch is delayed and simply said, the company loses money.
Thousands of businesses worldwide are dependent on a good talent pool to hire from. This means that the whole world will be adopting new technologies like machine learning, AI, cloud, and others at a slower pace. The software development growth can’t keep up with the shortage of engineers.
Whatever can go wrong, will go wrong – Murphy’s Law
Are software developers in demand? Yes, but!
The talent shortage of software developers is only a small part of the whole story. Employers face many more challenges when it comes to the Software Development industry.
Even when companies manage to find a pool of a dozen software developers to choose from, they face these challenges:
The shortlisted software developers don’t have enough experience
They don’t have all of the technical skills needed for the job
They don’t have soft skills (communication, problem-solving, teamwork, leadership, work ethic, flexibility and so on)
They don’t have formal education
The salary demands are outrageous
The shortlisted software developers don’t have enough experience
We have analyzed the market. Many people are recent software developer graduates, and they are new to the marketplace. Yes, we were all at this point once in our lives, but you will need the experience to keep the reputation of your company and the standards you set high.
There are times when you can hire inexperienced software developers because of the shortage, but you can’t expect high-quality work to be done by them in the next months or even years.
These people aren’t problem solvers, and your team will waste more time to explain everything to them than do actual work. It’s not cost-effective.
They don’t have all of the technical skills needed for the job
When searching for new software developers for your company, you will find that more often than not, they won’t have the technical skill needed to complete the necessary work.
A software developer skilled in one field might be lacking in another. Depending on your project, maybe he will do the current job well, but he won’t be able to do the next two projects.
You need to put these people to tests, have them talk to the HR department, basically lose a lot of time, and you might end up with the wrong person.
They don’t have soft skills
Soft skills are almost as important as technical skills. They complement each other. Maybe you’ll find a great software developer who simply doesn’t like talking to people. He won’t share his thoughts with the team or explain in what direction his work is heading. Because of his lack of teamwork and communication, your project might end up being a mess. This is especially true when it comes to larger projects.
Working for a software development company isn’t solo work. People are diverse, and they can complement each other with their work. But that only works if they both have soft skills in the first place.
They don’t have formal education
The majority of schools in the world, including the USA, don’t teach computer science. Data shows that 58% of all new jobs are STEM jobs (Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics). It’s the most significant job field in the world, and schools aren’t adapting. This is especially true for schools in the USA.
Many software developers don’t have a formal education. Even though they do have skills to complete some projects, they have some disadvantages to those with formal education.
Those with formal education understand algorithms and data structures. They have experience with compilers and interpreters. They are trained in OS theory; they know how operating systems software works, and they understand different architectures. Big companies have firsthand experience of this difference when big complicated things arise. The problem-solving skills and critical algorithms are simply better.
That’s when you understand that when people say that formal education teaches you things that “don’t have real-world application,” are either lazy or not competent enough to understand those things.
The salary demands are outrageous
With so much demand for software developers and such a small pool to choose from, they are free to demand high salaries for their services. Everyone needs to be paid well for their work, but companies have to secure their stability first.
When buying products online or in brick and mortar shops, you always look for quality. You don’t want to pay something that will only last a few days or months if it’s supposed to last for years. The same is for your workers. You need to hire software developers, so their prices match their competency. Until the world (especially the USA) starts producing more talent, you will keep ending up with sloppy workers at a high price.
So, what’s the solution to successfully managing the software developer pool talent and managing all these challenges you face when hiring software developers?
Get rid of the talent shortage of software developers by hiring abroad. Yes, that means outsourcing.
How Can Outsourcing Help Your Company Overcome the Shortage of Software Developers?
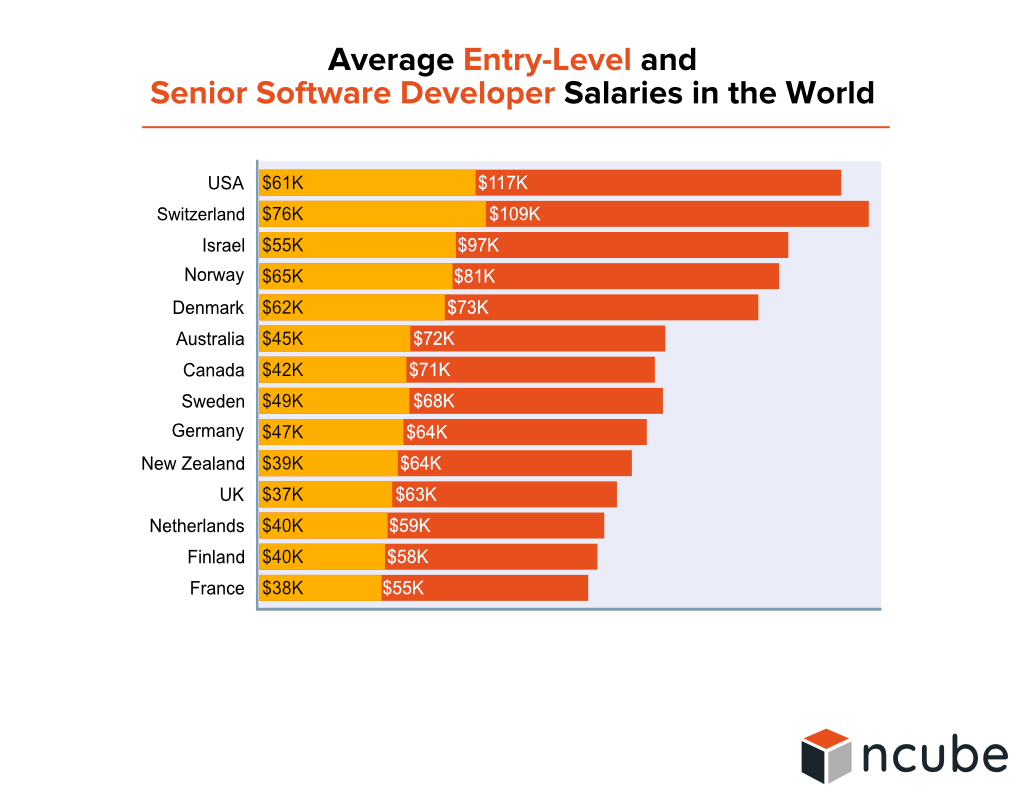
The shortage of local software developers is the number one reason companies decide to outsource. The second reason is the average salary expectations.
For example, outsourcing your work to Ukraine where our company is based will save you tens of thousands of dollars per each developer. This is a fact that can’t be ignored.
Virtual teams to Ukraine, particularly to our company NCube makes sense because of these reasons:
Available Talent
Cost
Convenient Time Zone (If you are from the USA, there is a 6-9 hours difference. When you sleep, we work and vice-versa. Less time lost on projects)
You can focus on your Core Business Development
Enhance service quality
Eastern Europe has a growing labor force of highly skilled software developers and other workers in the IT areas.
The general population speaks English and sometimes even a third language. This means there will never be communication problems.
NCube is the Way to Overcome the Software Developer Talent Shortage
Technology leaders around the world trust NCube to develop their products. We have over 30,000 developers in our network, and it only takes us 2-4 weeks to launch a team. We handpick specialists for your project, keep your intellectual property safe, and all our work is being reported directly to you and your company leaders.
NCube Statistics
11 years of software development experience
70% of our engineers are certified senior developers
86% of our engineers work on a project from start to finish
52% of our clients scale up during the first year of business
293% growth over the past three years
“Good talent is the driving force behind every project” – NCube

