Cloud has become ubiquitous, allowing companies to adapt to the rapidly changing market needs and provide top-notch customer experience.
If you’re considering moving your business to the cloud, you’ve probably heard of IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
They are cloud service models. If you’re not yet familiar with the topic, here are some advantages of cloud services as compared to the on-premises solution.
- Lower cost. Cloud computing takes out the need for maintaining hardware infrastructure. There’s no need to build out massive data centers and hire a development team to handle them. With cloud solutions, any features can be used on-demand.
- Scalability. On-premises solutions are hard to upgrade, whereas cloud-based services can be adjusted to respond to heavy traffic, peak loads and other needs. You can actually scale up or back in a matter of seconds.
- Availability. Cloud solutions are available upon payment and no added configuration is required. You can use them right away.
- Security. Cloud-based services come with highly secure data encryption, networking firewalls and advanced tools to prevent breaches. Moreover, data is backed up and can be easily restored.
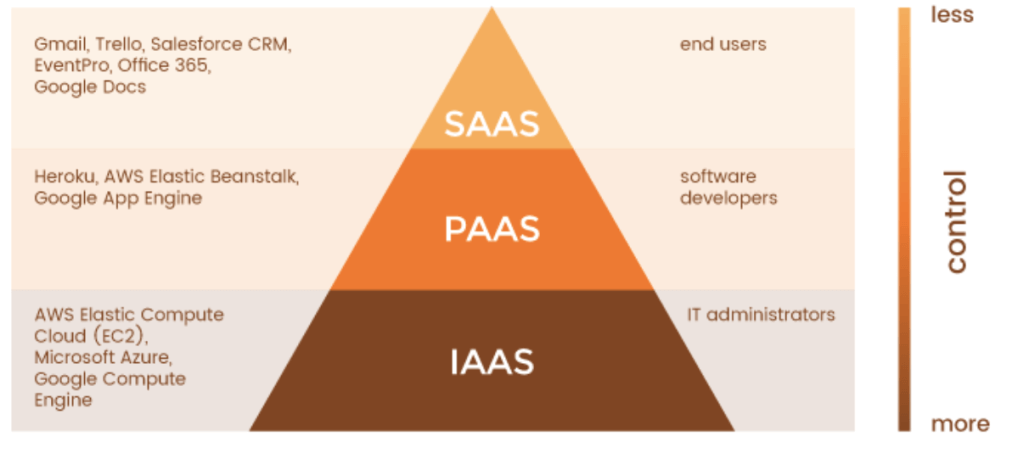
What are SaaS, PaaS and IaaS? In brief
SaaS. Software as a Service implies that all basic system settings are managed by the vendor, and the client can access the application via the Internet connection.
PaaS. Platform as a Service means that the server’s operating system is managed by the vendor, and the client only has control over the applications.
IaaS. Infrastructure as a Service. The client receives virtual servers and a virtual network upon which they can install software.
In this article, we will investigate the difference between SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. Here’s an infographic if you are here for a quick look.
What is SaaS?
Within the SaaS model, the product is hosted by the provider and is available to customers through a browser or API.
Most often, the product is a cloud solution that resembles a traditional software application, except it’s deployed from the vendor and its support rests on that vendor. Moreover, the SaaS vendor manages the following elements (actually all of them):
- Software product
- Runtime
- Integrations
- OS
- Virtualization
- Security
- Databases
- Hardware maintenance
- Storage
The customer just needs to connect to the Internet, log in to the account, and use the product.
Software-as-a-service advantages
As an out-of-the-box solution, SaaS products empower particular elements of business processes. Think CRM, sales management and HR platforms, and email systems. As a business model, the advantage of SaaS is getting a stable income in the form of monthly or yearly payments from loyal users.
SaaS for business is beneficial due to a low cost of ownership: you only pay for using the version of the service. There’s no need to spend money on the development of your own product and hiring technical specialists.
Another strong side of SaaS products is their availability. Because the product is located on the vendor’s servers, a user can access it remotely using any device, and the data is stored and encrypted on the vendor’s side.
SaaS examples
The most prominent SaaS applications are project management systems, document management systems, and various online organizers. These tools have become a part of our daily lives.
Take Google Docs, for example, a tool that millions of people are using as we speak. Google provides the opportunity to plug in and work in Word, Excel from any device, solo or collaboratively. Unlike its desktop analogs, there’s no need to go through all the hoops like buying a license and installing the product.
What is PaaS?
Platform-as-a-service operates at a different level. While SaaS provides users with a full-fledged product, PaaS refers to a runtime environment that they can use to create their own apps.
Platform as a Service has integrated software components designed for building software. With a PaaS solution in place, you don’t need to build out and maintain the infrastructure needed for software development.
It has largely simplified software development. PaaS allows developers to deploy applications without the underlying necessities such as operating systems, servers, databases and development tools.
Simply put, PaaS is a foundation upon which a software product can be built.
Let’s see what elements are covered by the vendor:
- Development tools
- OS
- Virtualization
- Runtime
- Storage
- Networking
- Database
- Middleware
The customer, on the other hand, obtains control over applications and data.
Platform as a Service advantages
The definition of PaaS itself can stand as a benefit.
- Companies get an environment where they can create and launch new applications, without spending resources on building their own infrastructure. As such, they can get a jump on time-to-market.
- With PaaS, developers can quickly test new programming languages, OS, databases, and other development technologies.
- Companies can manage their applications and data, having complete control over them, which is not the case with SaaS applications.
PaaS examples
The commonly used PaaS applications are Google App Engine, Heroku, IBM Watson Cloud, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Magento Commerce Cloud, among others. The latter is widely used in e-commerce – its source code is accessible to developers and fully customizable to cater to the needs of e-commerce businesses.
What is IaaS?
Infrastructure as a Service is a cloud-based model that offers a full-fledged computing infrastructure (servers, data warehousing, networks, operating systems) designed for the deployment and launch of users’ software solutions.
How does IaaS work?
With IaaS, the client uses a virtual network or virtual server and can install any software application.
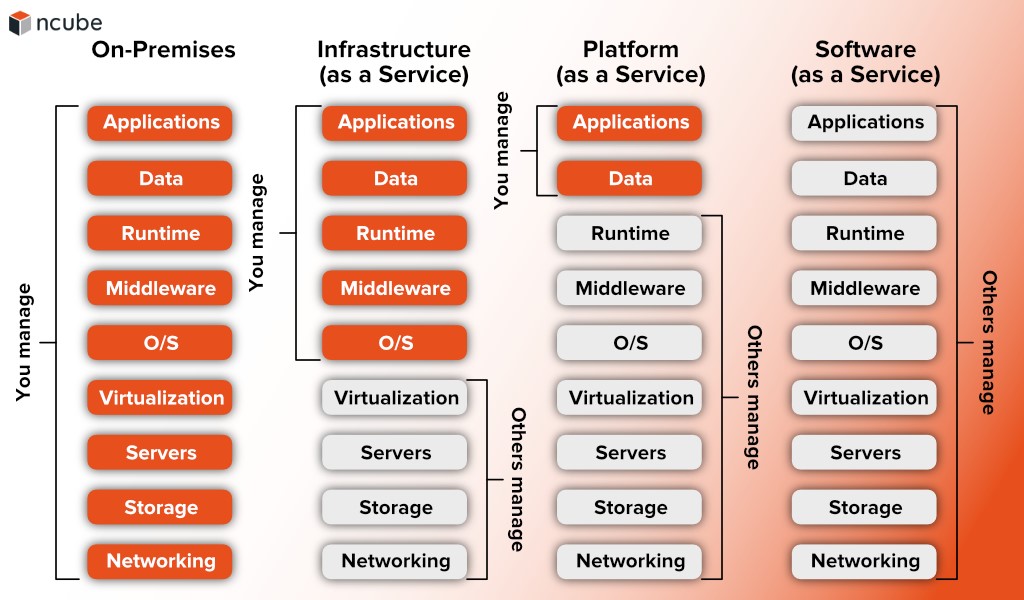
Let’s compare it with other models. SaaS only provides the interface, PaaS lets you use the environment, and IaaS comes with a complete computing infrastructure: servers, data storage, and networking hardware together with maintenance and support. It’s a whole another level in terms of operational scope that makes IaaS the most versatile and flexible of all models.
Managed by customer:
- OS
- Applications
- Data
- Runtime
- Middleware
Managed by vendor:
- Servers
- Storage
- Networking
- Virtualization
Infrastructure-as-a-service advantages
- Optimized budget. The IaaS cloud model eliminates the need to deploy on-premise hardware and software.
- Scalability boost. IaaS is extremely flexible, which allows you to scale the computing resources up or down as you go.
- Easy deployment. IaaS simplifies the deployment of the servers, processing, storage, and networking to get the infrastructure set up in no time.
- Control. Companies rely on this model to retain control over each aspect of the process: applications, data, runtime, operational systems.
IaaS examples
Some IaaS applications and services are DigitalOcean, Linode, Rackspace, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Cisco Metapod, Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine (GCE).
IaaS cloud service providers manage servers, storage, networking, and virtualization. The client controls applications, runtime, operational systems, data, and middleware. Here are some cases when opting for IaaS is the best solution:
- A company has an occasional need for additional IT resources.
- A company, usually a startup, cannot afford to purchase their own hardware and setting up an infrastructure.
- An organization is growing fast, and scaling up an infrastructure becomes a necessity.
- A company wants to verify an idea, so there’s no need to allocate IT resources.
SaaS, PaaS and IaaS comparison
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS: Which Cloud Service Is Suitable for You?
To summarize, choose the cloud model that resonates with your business needs.
- Opt for IaaS when you want to have control over the infrastructure and cannot afford your own servers. As such, you will move from CAPEX to OPEX.
- PaaS simplifies things for software developers, and thus increases time-to-market. Developers will enjoy the platform with convenient tools.
- Choose SaaS solutions when you need a tool for a specific task like a CRM, email, and collaboration tools. As such, you don’t have to go through the trouble of developing your own tools when you can use ready-made solutions.
